The Complete Guide to Laser Welding
 Sep. 05, 2025
Sep. 05, 2025
Laser welding is an advanced welding technique widely recognized for its precision, speed, and efficiency in joining metals. Its ability to produce strong, clean welds across a variety of materials has made it a preferred method in industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to electronics and medical device manufacturing.
Whether you are new to laser welding or seeking to optimize your existing setup, understanding the principles and equipment behind this technology is crucial for achieving consistent, high-quality results.
What Is Laser Welding?
Laser welding is a high-precision process that uses a focused laser beam to fuse metal pieces together. By delivering a concentrated heat source to a small area, laser welding produces narrow, deep welds with minimal distortion. It is particularly effective for thin materials and is valued for its repeatable, high-quality welds.
5 Types of Laser Welding
Different laser welding methods are suited for various applications and materials. Choosing the right type ensures efficiency, strength, and precision.
Spot Welding
Laser spot welding creates welds at precise points using short, high-energy pulses. It is ideal for tasks requiring pinpoint accuracy, such as battery packs and electronics assembly.
Scanner Laser Welding
This technique uses mirrors to rapidly direct the laser beam over the workpiece, enabling ultra-fast welding for complex or repetitive patterns. It is commonly used in high-speed production environments.
Keyhole Welding
Keyhole welding uses high power density to vaporize material and form a deep, narrow weld. It is suitable for thicker metals and applications demanding high penetration and strength.
Conduction-Limited Welding
Using lower energy than keyhole welding, this method heats the material without vaporizing it, producing a shallower weld. It is ideal for delicate or thin components.
Seam Welding
Seam welding produces continuous welds along a joint. It is frequently used in automotive and industrial manufacturing where long, uninterrupted welds are required for both strength and aesthetics.
Advantages of Laser Welding
Laser welding offers several benefits beyond speed and accuracy:
High Welding Speed: Accelerates production, helping meet tight deadlines.
Minimal Heat-Affected Zones: Reduces distortion and preserves surrounding material integrity.
Superior Weld Quality: Produces clean, consistent, and strong welds with minimal post-processing.
Versatility: Works on a wide range of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and titanium.
Non-Contact Process: Minimizes tool wear and enables welding of delicate or irregular parts.
Energy Efficiency: Consumes less energy and lowers operational costs compared to traditional welding.
Automation Ready: Easily integrates with robotic systems for efficient, automated production.
These benefits make laser welding systems suitable for both handheld and automated applications.
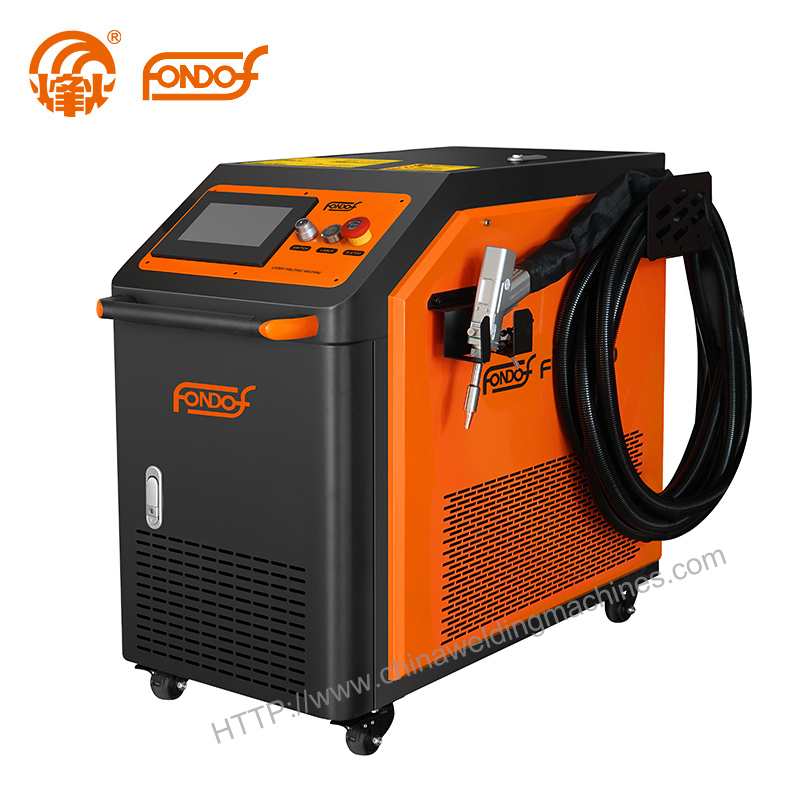
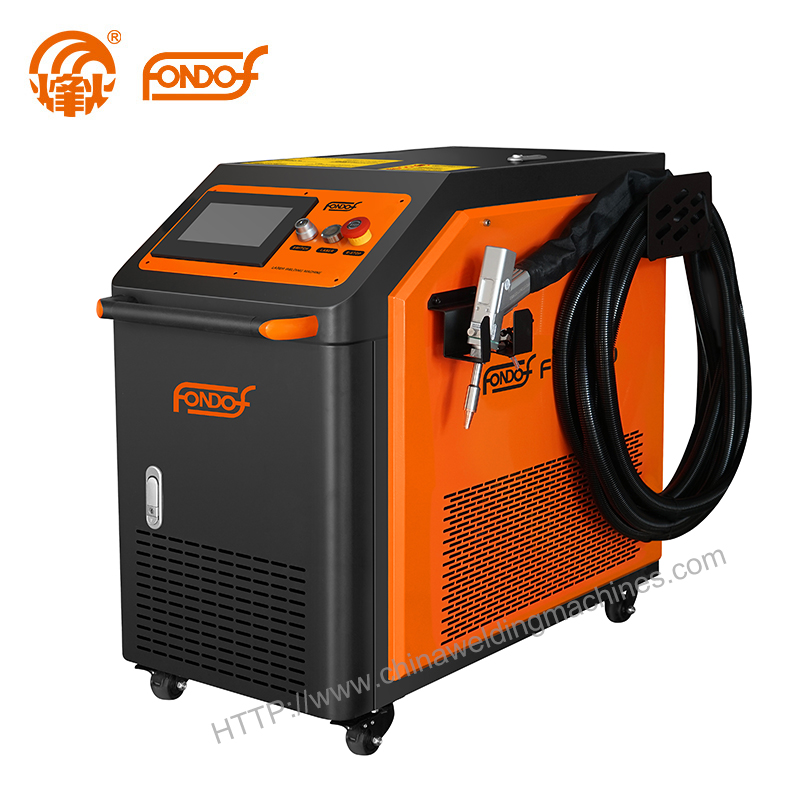
Key Components of Laser Welding Systems
To maximize performance, understanding the essential equipment is important:
Laser Source
The laser source generates the beam used for welding. Common types include fiber lasers, CO2 lasers, and solid-state lasers, each offering unique advantages in efficiency, material compatibility, and longevity.
Beam Delivery System
This system focuses and guides the laser onto the workpiece using fiber optics, mirrors, or lenses to ensure precise weld placement and consistent power.
Motion Control System
Robotics, linear actuators, or gantries control the movement between the laser and material. Precision motion systems are critical for repeatable, accurate welds.
Shielding Gas Supply
Argon, nitrogen, or other gases prevent oxidation and contamination at the weld site, ensuring strong and clean joints.
Cooling System
Laser welding generates heat that requires effective cooling—typically water-based—to maintain equipment performance and extend its lifespan.
Safety Enclosures
Enclosures protect operators from laser beams and harmful fumes. Many systems include interlocks and filters for enhanced safety in high-power or automated operations.
Proper integration of all components ensures reliable, high-quality welding results while maintaining a safe working environment.
Common Applications of Laser Welding
The precision and versatility of laser welding make it essential in many industries:
Automotive: Strong, accurate welds in car bodies, transmissions, and exhaust systems.
Medical Devices: Joining tiny components such as surgical instruments and implants.
Aerospace: Lightweight, durable welds on turbine blades and structural parts.
Electronics: Clean welds on heat-sensitive components.
Jewelry: High-precision welding for gold, silver, and other precious metals.
Battery and Energy: Joining battery cells, particularly for electric vehicle applications.
These examples demonstrate the broad value of laser welding across modern manufacturing sectors.
Maximizing Laser Welding Performance
Whether implementing a new system or upgrading existing equipment, proper selection, setup, and maintenance of laser welding machines are key to boosting efficiency, weld quality, and overall productivity. Prioritizing safety, equipment compatibility, and automation potential ensures that your operations stay competitive and cost-effective.