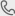Is Pulse TIG Welding Better?
 Apr. 09, 2024
Apr. 09, 2024
Welding processes have undergone significant advancements over the years, with manufacturers continually striving to improve efficiency, quality, and versatility. One such innovation is pulse TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, which has gained popularity for its ability to enhance control, reduce heat input, and produce high-quality welds. In this article, we delve into the characteristics, advantages, and considerations of pulse TIG welding to determine whether it holds superiority over traditional TIG methods.
Understanding Pulse TIG Welding
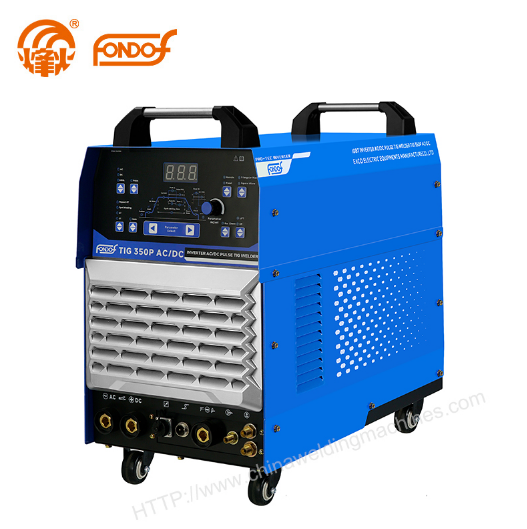
Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is a popular method known for its precision and versatility. Traditional TIG welding involves a constant electrical current flowing between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece, creating the weld. Pulse TIG welder, on the other hand, introduces intermittent pulses of current into the welding arc.
How Pulse TIG Works
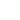
In pulse TIG welding, the welding machine rapidly switches between a high peak current (pulse) and a low background current. During the pulse phase, the high current generates intense heat, effectively melting the base metals and creating a deep penetration into the workpiece. The background current then maintains the arc, allowing the weld pool to cool slightly before the next pulse. This cycle repeats, resulting in a controlled weld bead formation with reduced heat-affected zones.
Benefits of Pulse TIG Welding
1. Heat Control:
Pulse TIG welding allows for greater control over heat input compared to traditional TIG welding. By pulsing the current, welders can alternate between high and low heat settings, reducing the overall heat input into the workpiece. This precise control is especially beneficial when working with thin materials or when welding intricate joints, minimizing the risk of warping, distortion, or burn-through.
Pulsed TIG lets you drastically improve heat control. As a result, you'll have fewer failed welds and less need for rework. Sometimes, this can save you a lot of money because metals like stainless steel, chromoly, or aluminum are not cheap, especially if they were machined before welding.
If you need to weld quickly and cleanly without breaking an edge or filling a hole with filler metal, pulsing is another great way to give you extra control and accuracy in difficult weld locations. Without a good steady pulse during TIG welding, heat builds up and starts to melt the metal.
2. Reduced Heat Affected Zone (HAZ):
The ability to control heat input in pulse TIG welding results in a smaller Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) compared to conventional TIG welding. A smaller HAZ means less thermal stress on the base material, preserving its mechanical properties and reducing the need for post-weld heat treatment.
3. Improved Weld Quality:
Pulse TIG welding often yields superior weld quality, with cleaner, smoother weld beads and improved fusion. The precise control over heat input and deposition allows for better penetration and fusion, resulting in stronger, more aesthetically pleasing welds.
4. Increased Welding Speed:
While traditional TIG welding requires a steady hand and a slower welding speed to maintain control over the weld pool, pulse TIG welding can be performed at higher speeds without sacrificing quality. The intermittent pulses of current provide rapid cooling intervals, allowing for faster travel speeds while still achieving satisfactory weld penetration and fusion.
Limitations of Pulse TIG Welding
Despite its numerous advantages, pulse TIG welding is not without its limitations:
1. Complexity:
Pulse TIG welding systems are often more complex and expensive than traditional TIG welding equipment. They require additional controls and settings to adjust parameters such as pulse frequency, pulse width, and peak current, necessitating proper training and expertise to utilize effectively.
2. Equipment Compatibility:
Pulse TIG welding may not be suitable for all applications or materials. Certain materials and thicknesses may require specific pulse settings or may not be compatible with pulse welding altogether. Additionally, existing TIG welding equipment may need to be upgraded or modified to accommodate pulse welding capabilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, TIG welder with pulse offers several distinct advantages over traditional TIG welding, including improved heat control, reduced heat affected zone, enhanced weld quality, and increased welding speed. These benefits make pulse TIG welding particularly well-suited for applications requiring precision, efficiency, and high-quality welds. However, it's essential to consider the complexity of pulse TIG welding systems and their compatibility with specific materials and applications.
As with any welding technique, choosing the right method depends on factors such as the specific requirements of the project, the skill level of the welder, and the available equipment. Ultimately, Pulse TIG welding can be a valuable addition to a welder's repertoire, offering enhanced capabilities and the potential for superior results.
For more information on Pulse TIG welders or to find a reliable supplier, please don't hesitate to contact us.